Table of Contents
Apache HTTP Server
General Information
Installation and configuration of Apache web server.
Checklist
- Distro(s): Enterprise Linux 6/7
Installation
Installing apache web server is very simple and can be done via repos or compiling. Repos is easier, while compiling usually provides newer versions.
Repo: EPEL
- CentOS 6.7: Apache 2.2
- CentOS 7.2: Apache 2.4
For an easy standard Apache install, the repo install method is used. These packages are older, but stable.
Install package
yum install httpd
Start the service and enable on boot
- EL 6
service httpd start chkconfig httpd on
- EL 7
systemctl start httpd systemctl enable httpd
SSL
To add SSL support, install the “mod_ssl” package:
yum -y install mod_ssl
Repo: Software Collections
Versions as of 04/13/2016:
- httpd 2.4
- Add the software collections repo.
- Install
yum install httpd24 - Enable the software collection
scl enable httpd24 bash
- Control operation as below.
Compile and Install
If you need a newer feature than what is available in the repo installed versions, you may need to compile and install.
Prerequisites
- Install gcc in order to compile packages
yum install gcc
- Install apr-devel, apr-util-devel, and pcre-devel
yum install apr-devel apr-util-devel pcre-devel- apr = Apache Portable Runtime
- pcre = Perl-Compatible Regular Expressions Library
- If you really want to compile these as well for newer versions, see here: http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/install.html#requirements
Install Procedure
- Download
- Visit the download page: http://httpd.apache.org/download.cgi
- Wget a link to the desired version(example with a mirror)
wget http://www.webhostingjams.com/mirror/apache/httpd/httpd-2.4.18.tar.gz
- Extract Apache
tar -zxvf httpd-2.4.18.tar.gz cd httpd-2.4.18
- Configure Apache from httpd-2.4.18/
./configure --prefix=PREFIX
- –prefix=PREFIX ⇒ Where “PREFIX” is the directory where you want Apache to be installed, such as “/opt/apache”
- Compile
make - Install
make install
- Customize web server
vim PREFIX/conf/httpd.conf
- Start web server
PREFIX/bin/apachectl -k start
Configuration
The default configuration:
- Main Config: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- Additional Config: /etc/httpd/conf.d/
- This is usually used for add on modules config
httpd.conf - Global Configs
Some common defaults to change in /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf:
Listen to specific IP instead of all
Listen 10.1.2.3:80
- Default: Listen 80
Set ServerName
ServerName example.com:80
- Default: Commented and attempts to auto determine (not always accurate)
NameVirtualHost to specific IP instead of all (if using virtual hosts)
NameVirtualHost 10.1.2.3:80
- Default: NameVirtualHost *:80 (and commented out)
Security Configs
##-- Security --## #- Information Disclosure -# ServerTokens Prod ServerSignature Off # FileETag: File attributes used to create the ETag HTTP response header for static files FileETag -INode +MTime +Size #- Web Application Security -# # Trace/Track - disabled for security purposes TraceEnable Off # Cross-Frame Scripting prevention (click jacking) # DENY = Deny all attempts to frame the page Header always append X-Frame-Options DENY # Cross Site Scripting protection Header set X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" Header edit Set-Cookie ^(.*)$ $1;HttpOnly;Secure ##-- End of Security Settings --##
ssl.conf
The SSL config file is located here: /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf
SSL Certificate and Certificate Authority
SSLCertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/localhost.crt SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/pki/tls/private/localhost.key SSLCertificateChainFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/server-chain.crt
- Above are defaults, change to location of cert, key and CA cert
Protocol and Ciphers
SSLProtocol TLSv1.2 SSLCipherSuite HIGH:!MEDIUM:!3DES:!ADH:!AECDH:!DHE:!EDH:!RC4
- Default SSLProtocol: all -SSLv2
- Default SSLCipherSuite: DEFAULT:!EXP:!SSLv2:!DES:!IDEA:!SEED:+3DES
Enable SSL Cipher Honoring (server picks the strongest compatible cipher)
SSLHonorCipherOrder on
Other Security Settings
Other important security settings.
Redirect HTTP to HTTPS
Redirect all HTTP to HTTPS
<VirtualHost *:80> ServerName example.com <IfModule mod_rewrite.c> RewriteEngine On RewriteCond %{HTTPS} off RewriteRule (.*) https://%{HTTP_HOST}%{REQUEST_URI} </IfModule> </VirtualHost>
HSTS
Enabling HTTPS Strict Transport Security (HSTS).
Add the strict transport security header to the listening HTTPS host section
# Optionally load the headers module: LoadModule headers_module modules/mod_headers.so <VirtualHost *:443> Header always set Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=63072000; includeSubdomains;" </VirtualHost>
- max-age=63072000 → Tell web browsers to connect to the site using HTTPS only for two years. Countdown is reset each time the site is visited.
Virtual Hosts: Multiple Domains
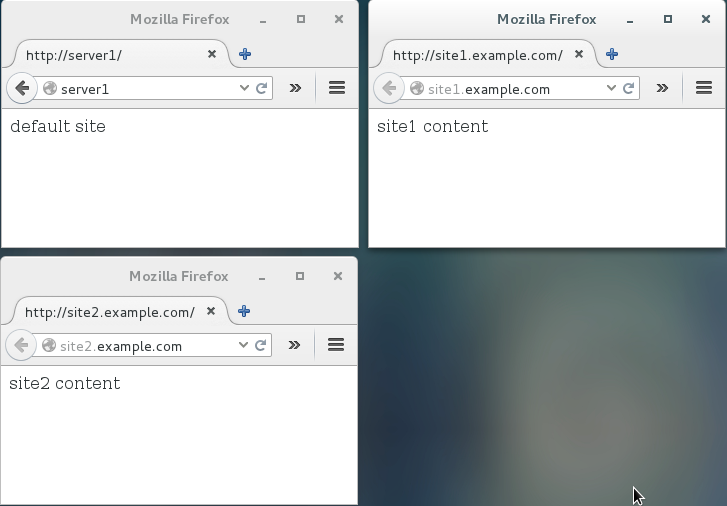
You can host multiple web sites, each with their own domain, from the same Apache instance by using virtual hosts directives.
Example sites
- server1 ⇒ the server's normal dns entry and “default” virtual host.
- site1.example.com ⇒ virtual host
- site2.example.com ⇒ virtual host
- Create a new file: /etc/httpd/conf.d/virtual_hosts.conf
# Directory for virtual host sites <Directory "/www"> Options Indexes FollowSymLinks AllowOverride None Require all granted </Directory> # Default catch all <VirtualHost _default_:80> DocumentRoot /www/default </VirtualHost> # Site 1 <VirtualHost *:80> ServerName site1.example.com DocumentRoot /www/site1 ServerAdmin webmaster@site1.example.com ErrorLog logs/site1.example.com-error_log CustomLog logs/site1.example.com-access_log common </VirtualHost> # Site 2 <VirtualHost *:80> ServerName site2.example.com DocumentRoot /www/site2 ServerAdmin webmaster@site2.example.com ErrorLog logs/site2.example.com-error_log CustomLog logs/site2.example.com-access_log common </VirtualHost>
- Create the new directories
mkdir -p /www/{default,site1,site2}
- Create test indexes
echo "default site" > /www/default/index.html echo "site1 content" > /www/site1/index.html echo "site2 content" > /www/site2/index.html
- Reload Apache config files
apachectl graceful - DNS entries will need to be made (/etc/hosts for demonstration purposes)
vim /etc/hosts 192.168.1.150 server1 site1.example.com site2.example.com
Virtual Hosts: Single Domain with Site Sub Dirs
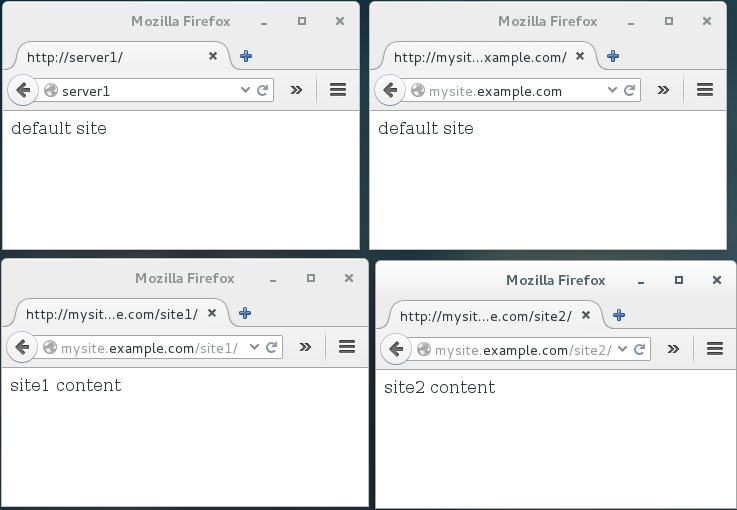
An alternative to separate sub-domains, is a single domain with sub directories hosting different sites.
Example Sites
- server1 ⇒ the server's normal dns entry and “default” virtual host
- mysite.example.com ⇒ main site and “default” virtual host
- mysite.example.com/site1 ⇒ site 1
- mysite.example.com/site2 ⇒ site 2
- Create a new file: /etc/httpd/conf.d/virtual_hosts.conf
# Directory for virtual host sites <Directory "/www"> Options Indexes FollowSymLinks AllowOverride None Require all granted </Directory> # Default catch all <VirtualHost _default_:80> DocumentRoot /www/default ServerName mysite.example.com ServerAdmin webmaster@mysite.example.com ErrorLog logs/mysite.example.com-error_log CustomLog logs/mysite.example.com-access_log common # Site 1 Alias /site1 /www/site1 SetEnvIf Request_URI "^/site1/.*$" site1_log CustomLog logs/site1-access_log common env=site1_log <Directory "/www/site1"> Require all granted </Directory> # Site 2 Alias /site2 /www/site2 SetEnvIf Request_URI "^/site2/.*$" site2_log CustomLog logs/site2-access_log common env=site2_log <Directory "/www/site2"> Require all granted </Directory> </VirtualHost>
- Create the new directories
mkdir -p /www/{default,site1,site2}
- Create test indexes
echo "default site" > /www/default/index.html echo "site1 content" > /www/site1/index.html echo "site2 content" > /www/site2/index.html
- Reload Apache config files
apachectl graceful - DNS entries will need to be made (/etc/hosts for demonstration purposes)
vim /etc/hosts 192.168.1.150 server1 mysite.example.com
Operation
Controlling the Apache httpd service: Apache recommends using the “apachectl” signals instead of the OS service control interface (service/systemctl).
- After sending a signal to httpd, watch its progress in the error_log file: logs/error_log
Start
- Check syntax, if errors are found, refuse to start.
- Start the httpd process and start the number of workers specified on the config files via the “StartServers <number>” directive.
apachectl -k start
Stop
- Immediately stop the httpd process and kill workers.
- User connections in progress are terminated.
apachectl -k stop
Graceful Restart
- Check syntax, if errors are found, refuse to restart.
- Parent process advises that workers shutdown after their current requests.
- Once all workers have finished and exited, start up.
- This does not interrupt user connections.
apachectl -k graceful
Restart
- Check syntax, if errors are found, refuse to restart.
- Parent process kills workers, then starts up.
- This interrupts user connections.
apachectl -k restart
Graceful Stop
- Parent process advises that workers shutdown after their current requests.
- New requests are not accepted.
- This does not interrupt user connections.
apachectl -k graceful-stop